What is Fatty Liver And How To Diagnose It?
March 4, 2024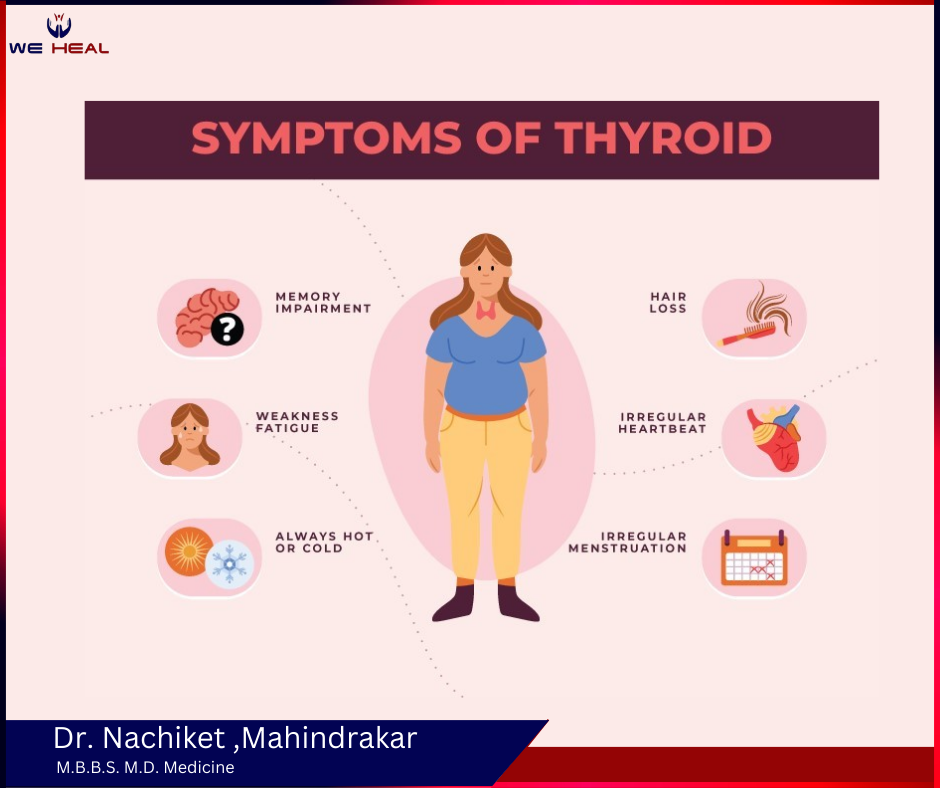
Thyroid Tests: Understanding Your Levels and What They Mean
March 18, 2024Diabetes, a chronic condition that affects millions worldwide, is characterised by high blood sugar levels. It is more than just a health issue, it is a lifestyle concern. With appropriate measures, you can manage diabetes effectively, leading to a healthier, happier life. In this article, we explain what diabetes is, its causes, symptoms, potential health risks, and ways to control it.
What is diabetes?
Diabetes is a chronic health condition that occurs when your body cannot use or produce enough insulin, which is a hormone that regulates the amount of sugar in your blood. There are two primary types of diabetes: type 1 and type 2.
Statistics (Singapore)
Diabetes is a serious health issue in Singapore. According to the National Health Survey 2020, about 11.3 percent of Singapore residents aged 18–69 have diabetes.
What causes diabetes?
While the exact causes vary depending on the type of diabetes, common factors include genetic predisposition, environmental factors, lifestyle choices, and obesity.
What are type 1 and 2 diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes
It is usually diagnosed in children and young adults, and it occurs when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas.
Type 2 diabetes
It is the most common form, develops when the body becomes resistant to insulin or when the pancreas cannot produce enough insulin. This type often stems from obesity and lack of physical activity.
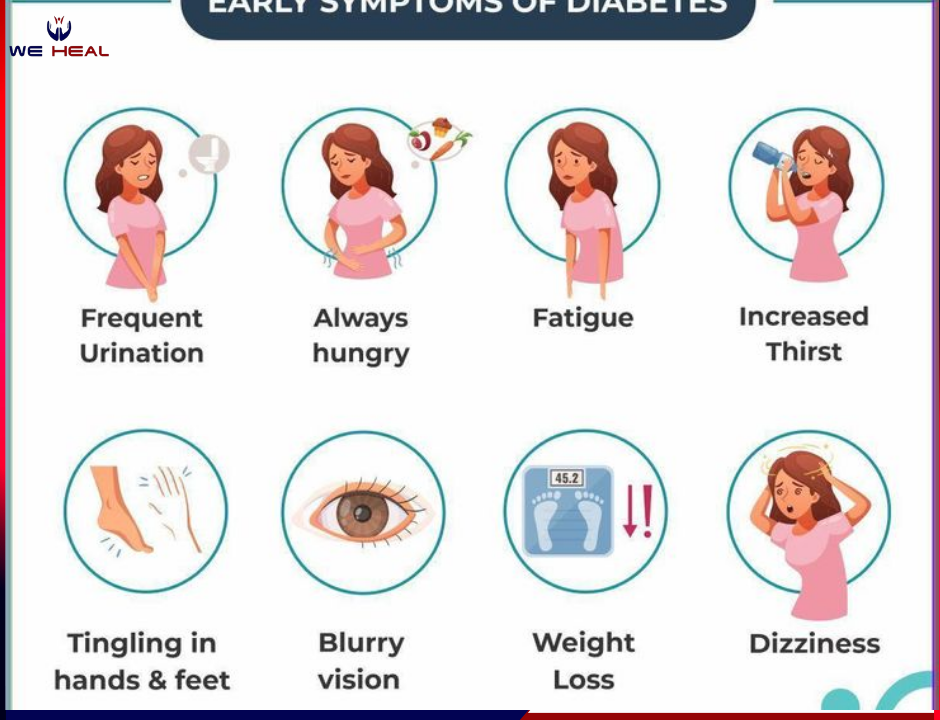
What are the symptoms of diabetes?
Common symptoms include increased thirst and urination, extreme hunger, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, blurred vision, and frequent infections. However, some people with diabetes do not show any symptom, particularly those with type 2 diabetes.
What are the potential health risks?
Diabetes can lead to severe health complications, including heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, eye problems, and nerve damage. Therefore, effective diabetes management is critical to minimizing these risks.

Controlling diabetes
Managing diabetes often requires a multi-faceted approach, including:
- Healthy eating: Follow a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein.
- Regular physical activity: Exercise helps maintain a healthy weight and can improve insulin sensitivity.
- Regular check-ups and monitoring: Monitoring your blood sugar levels and having checkups regularly are essential.
When to see a doctor?
If you exhibit symptoms of diabetes or have risk factors such as obesity, a family history of diabetes, or a sedentary lifestyle, consult a doctor. Find a Primary Care Network clinic near you for comprehensive care.