Causes Of High Blood Pressure- Hypertension- We Heal Clinic
April 8, 2024
Causes of Lung Pain and Treatment Options- We Heal Clinic
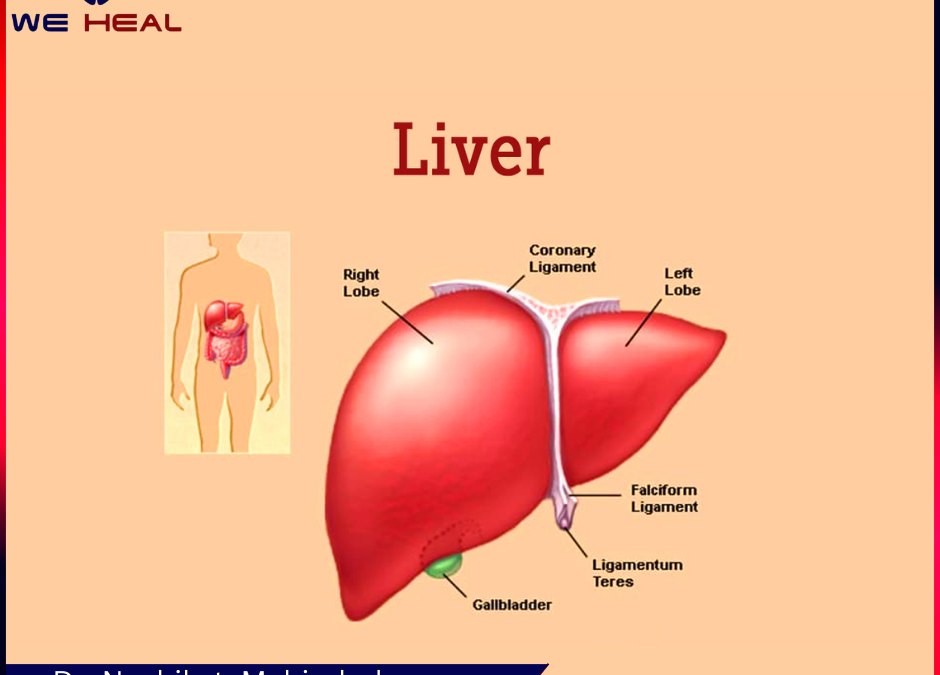
April 22, 2024- The liver, also known as the largest gland of a human body, is situated above the stomach, right kidney, and upper right region of the abdominal cavity, as well as just below the diaphragm. It is a sizable organ . It is reddish-brown in its appearance and weighs roughly 3 pounds. It also looks rubbery in its texture.
- The rib cage protects various organs from any kind of external damage; the liver is also protected due to the cover of the rib cage, as a result of which it is difficult for us to feel it in a normal condition.
- liver consists of two lobes: one is the right lobe and the other is the left lobe. Beneath the liver, a portion of pancreas, intestines and gallbladder are located. Along with these organs, it helps in various body functions such as breakdown, assimilation and processing of food.
Liver Functions
The liver is a vital organ that performs a wide range of important functions in the body. Some of the main functions of the liver include:
- Strengthen the Metabolism: The liver helps to metabolize carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, converting them into usable energy and storing it in the form of glycogen. It also metabolizes medications to make them more easily absorbed by the body.
- Helps in Detoxification: The liver’s primary function is to filter blood arriving from the digestive system. The liver helps to filter out toxins, such as drugs and alcohol, from the bloodstream and break them down into substances that can be eliminated from the body through urine or feces.
- Production of bile, which helps in fat digestion: The liver produces bile, a yellow-green fluid that helps to digest fats and absorb fat-soluble vitamins. The liver excretes bile and controls the majority of blood chemical levels. This aids in removing waste from the liver.
- Store Vitamins & Minerals: The liver stores a variety of substances, including vitamins, minerals, and sugars. It also stores iron, which is essential for the production of red blood cells.
- Helps in the Production and Regulation of Hormones: The liver plays a role in the production and regulation of various hormones, including insulin and testosterone.
- Helps in Blood Clotting: The liver produces substances that are essential for blood clotting, such as clotting factors and fibrinogen.
- Produce Nutrients: The liver receives all the blood that exits the intestines and stomach.
Overall, the liver is a crucial organ that performs a wide range of vital functions that are essential for maintaining good health.
Liver Diseases
- Hepatitis A: The hepatitis A virus is responsible for the highly contagious liver ailment known as hepatitis A. This particular hepatitis virus is one of many varieties that can inflame your liver and impair its capacity to operate.
- Hepatitis B: The hepatitis B virus, which causes hepatitis B, is a dangerous liver infection (HBV). Developing chronic hepatitis B raises your risk of getting liver cancer, liver failure, or cirrhosis, which causes the liver to become permanently scarred.
- Hepatitis C: A viral illness called hepatitis C can result in significant liver damage by inflaming the liver. Contaminated blood can spread the hepatitis C virus (HCV).
- Hepatitis D: The hepatitis D virus (HDV), which depends on HBV for reproduction, causes hepatitis D, an inflammation of the liver. The absence of the hepatitis B virus prevents hepatitis D infection. The co-infection of HDV and HBV is regarded as the most severe type of chronic viral hepatitis because it leads to hepatocellular cancer and liver-related mortality more quickly.
- Hepatitis E: Hepatitis E is a disease caused by the hepatitis E virus that results in liver inflammation (HEV). The fecal-oral route of transmission of the virus is primarily through contaminated water.