Knocked-Out Tooth: What to Do in the First Crucial Hour
December 16, 2024
Understanding the Causes of Different Types of Diabetes
December 30, 2024Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions worldwide, altering the body’s ability to process sugar effectively. While many associate diabetes with blood sugar levels, complications can extend beyond this—impacting major organs like the liver. At We Heal Clinic, Dr. Nachiket Mahindrakar, a renowned expert in internal medicine, sheds light on the intricate relationship between liver disease and diabetes.
Understanding the Connection Between Diabetes and Liver Disease
The liver plays a crucial role in regulating glucose and fat metabolism. In people with diabetes, particularly Type 2 diabetes, the risk of developing liver diseases is significantly higher. This connection stems from insulin resistance, a hallmark of Type 2 diabetes, which leads to the accumulation of fat in the liver and chronic inflammation.
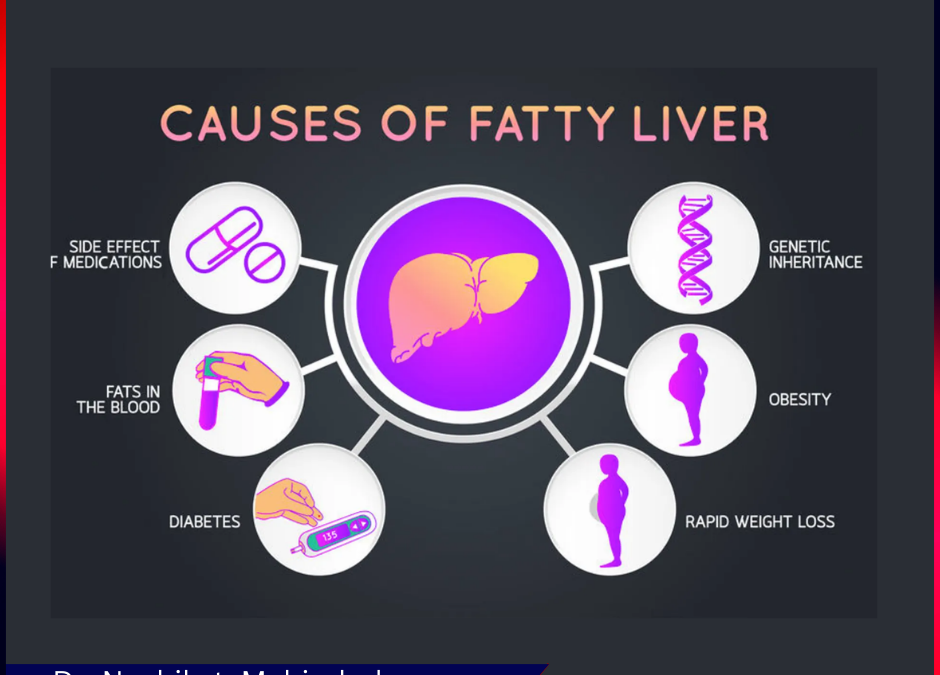
One of the most common liver complications associated with diabetes is non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). NAFLD encompasses a spectrum of liver conditions ranging from simple fat buildup to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), which can progress to liver fibrosis, cirrhosis, or even liver cancer.
Key Symptoms of Liver Disease in Diabetics
Liver disease often progresses silently, showing few or no symptoms in its early stages. However, as the condition advances, patients may experience:
- Fatigue
- Unexplained weight loss
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Swelling in the abdomen or legs
- Persistent abdominal pain
It is crucial to monitor these symptoms and seek medical attention if they occur.
Why Diabetics Are More Vulnerable
Several factors contribute to the increased risk of liver disease in diabetics:
- Obesity: Many individuals with Type 2 diabetes are also obese, which exacerbates fat accumulation in the liver.
- High Triglyceride Levels: Diabetes often leads to elevated blood fats, contributing to liver damage.
- Insulin Resistance: Impaired insulin signaling affects the liver’s ability to process sugar and fat efficiently.
Diagnosis and Monitoring
Dr. Nachiket Mahindrakar emphasizes the importance of regular screening for liver health in diabetic patients. Diagnostic tools include:
- Blood Tests: Liver function tests (LFTs) to check for abnormalities.
- Ultrasound: Detects fat deposits and structural changes in the liver.
- FibroScan: Assesses liver stiffness and potential scarring.
- Liver Biopsy: In rare cases, a sample may be taken to confirm the diagnosis.
Management and Treatment
The good news is that early detection and lifestyle modifications can significantly improve liver health. Dr. Mahindrakar recommends:
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats, while minimizing sugar and saturated fats.
- Weight Management: Losing even a small percentage of body weight can reduce liver fat.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity improves insulin sensitivity and reduces fat buildup.
- Medications: In some cases, medications to control blood sugar and cholesterol levels may be prescribed.
- Avoid Alcohol: Alcohol can exacerbate liver damage and should be avoided.
Prevention is Key
Preventive care is vital for reducing the risk of liver complications in diabetics. Regular check-ups, healthy lifestyle choices, and effective management of blood sugar levels form the cornerstone of prevention. Dr. Nachiket Mahindrakar’s expertise ensures personalized care tailored to each patient’s needs.
Conclusion
Liver disease is a common yet preventable complication of diabetes. Early intervention and comprehensive care can mitigate risks and enhance quality of life. If you’re living with diabetes and concerned about your liver health, consult Dr. Nachiket Mahindrakar at We Heal Clinic today for expert guidance.