What are the types of thyroid?
June 17, 2024
Thyroid Testing Demystified: Understanding TSH, T3, and T4 Levels
July 1, 2024Diabetes Mellitus is one of the most common chronic conditions affecting the human race. It is a condition mainly characterised by the presence of excessive amounts of glucose being present in the blood. Around 10% of the total population of humans have either type 1 or type 2 diabetes. Even though it is popular as a lifestyle disease occurring due to a sedentary lifestyle, lately, it has been seen to occur even in active individuals. The condition is more prevalent among the male population than the female.
This blog will help you understand the types of diabetes, some common and unusual diabetes symptoms, risk factors, and essential tips to manage diabetes.
Types of Diabetes
Diabetes insipidus and diabetes mellitus are the two types of diabetes. However, diabetes insipidus is a rare disorder where the kidneys cannot reabsorb water, causing excessive urination and thirst. A lack of vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone) causes it and is not related to diabetes mellitus, caused by insufficient insulin production or sensitivity leading to high blood sugar.
Diabetes mellitus is the most commonly occurring type of diabetes. It is a chronic metabolic cum endocrine disorder. Based on the utilisation of glucose content obtained from the food, there are mainly three types of diabetes mellitus:
- Type 1
- Type 2
- Gestational Diabetes.
-
Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes, also called juvenile or insulin-dependent diabetes, develops at a very young age. It occurs as an autoimmune disease where the body attacks its insulin-producing beta cells of the pancreas. As a result, the body becomes scarce of insulin as the pancreas cannot produce it. Individuals with Type 1 diabetes require regular insulin supplementation into their bloodstream to deal with this condition.
-
Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes mellitus is more common among adults than children. Thus, it is known as adult-onset diabetes. In this condition, the pancreas produces insulin, but only to a very limited amount compared to the typical body requirement. Along with the same, the body also shows a lack of response or exhibits insulin resistance. As a result, blood shows a higher concentration of glucose.
-
Gestational Diabetes
This type of diabetes develops during pregnancy. It happens when the body cannot make enough insulin during pregnancy, usually during the second or third trimester. This leads to high blood sugar levels, which can cause complications for both the mother and baby.
During pregnancy, the hormones produced by the placenta create insulin resistance in the body. This prevents the body from adequately utilising insulin for glucose metabolism. In normal conditions, the body produces enough insulin to overcome this resistance. However, in Gestational DM, the body cannot overcome the resistance.
Common Diabetes Symptoms
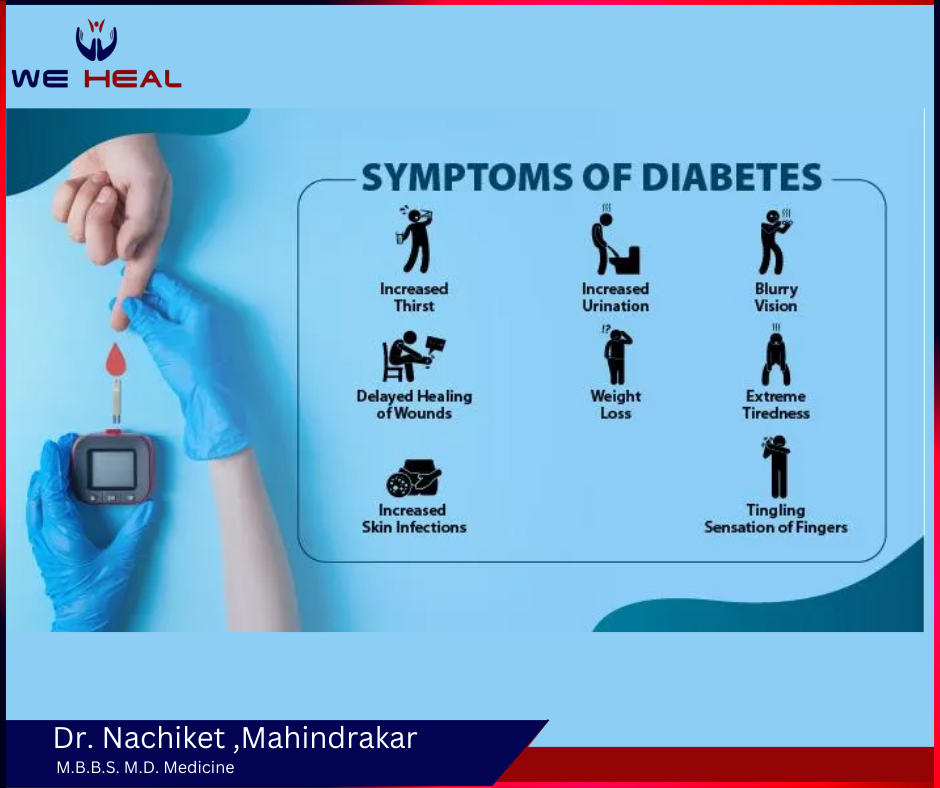
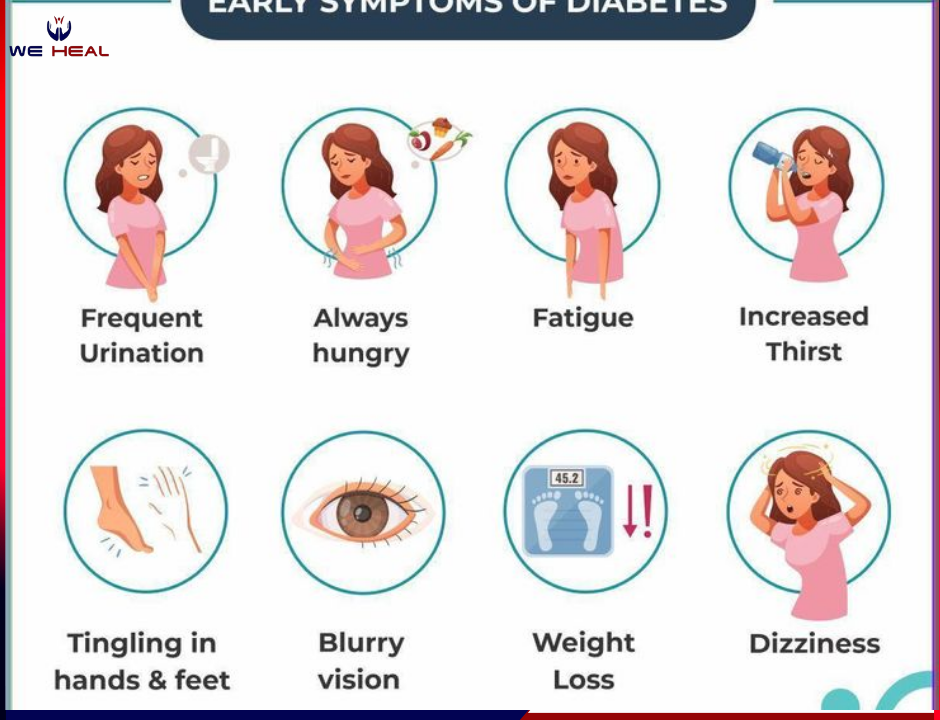
Irrespective of the type, there are a few common diabetes symptoms. They are:
- Polydipsia or increased thirst along with dryness of mouth
- Polyuria or increased frequency of micturition
- Blurry vision
- Delayed healing of wounds and sores
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue, tiredness, weakness
- Increased frequency of gum, skin or vaginal yeast infection
- Numbness or tingling sensation of fingers and toes.
A specific symptom of Type 1 diabetes mellitus includes bed wetting in children who previously did not wet the bed at night.
Polydipsia, polyuria and polyphagia (3Ps) are the three cardinal Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes symptoms. The same is seen in gestational DM. However, individuals with gestational Diabetes Mellitus have an increased nauseous feeling whenever they get an urge to eat.
Affected individuals may not show all the diabetes symptoms at the same time. Some may only exhibit a very few symptoms after a complete diagnosis from blood tests. The basic criteria for diagnosis is the occurrence of symptoms along with laboratory confirmation. The basic laboratory tests used for confirmation are:
| Test Name | Description | Normal Range | Prediabetic Range | Diabetes Indication |
| FBS (Fasting Blood Sugar) | Done after fasting for 6 hours. | 70-100 mg/dL | 100-125 mg/dL | Not applicable |
| PPBS (Postprandial Blood Sugar) | Blood glucose 2 hours after a meal. | 100-140 mg/dL | 140-190 mg/dL | Above 200 mg/dL |
| RBS (Random Blood Sugar) | Blood glucose is measured at any random time. | 70-140 mg/dL | Not applicable | Not applicable |
- HbA1C
HbA1C refers to glycated haemoglobin protein, specifically used to diagnose type 2 diabetes mellitus. The test helps in analysing diabetes with an average glucose level of the past 3 months.
| HbA1C level | Diagnosis |
| ≤ 5.7% | Normal levels |
| 5.7% – 6.4% | Prediabetic stage |
| above 6.4% | Indicative of diabetes and requires strict treatment and monitoring. |
Uncommon Symptoms and Warning Signs
Patients with diabetes normally express their symptoms primarily in the form of the 3Ps mentioned above. However, certain uncommon diabetes symptoms elicited include:
- Changes in gum in the form of Gingivitis
- Extreme dryness and burning sensation in the mouth
- Some may develop Parotiditis and candid infections
- Diabetic dermopathy or shin spots – These are harmless patches of oval or round shape with light red or brown colour.
- Numbness and tingling sensation in Extremities
- Decreased libido
Complications of Diabetes
Uncontrolled Type 2 diabetes mellitus can cause several complications, worsening the normalcy of life. The following are some of the expected complications of diabetes:
- Diabetic Retinopathy occurs when diabetes affects the ophthalmic system and blood supply to the eye.
- Diabetic Nephropathy occurs when diabetes mellitus affects the kidney and its nephrotic system.
- Diabetic Neuropathy: When diabetes mellitus affects the nervous system.
- Diabetic foot/ Gangrene / Diabetic foot ulcer: A complication resulting in tissue death of lower extremities that arises from an unhealed wound and gets worsened due to uncontrolled glucose in the blood.
- Increased risk of Cardiovascular diseases
- Hearing impairment
- Depression
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) is a life-threatening condition affecting Type 1 diabetes mellitus patients. Type 2 individuals are less prone to this condition, although chances are undeniable. Here, the body produces excessive amounts of blood ketones or acids.
Gestational Diabetes poses complications that affect both mother and child. These include:
- Delivery requires C-section
- Excessive birth weight
- Preeclampsia
- Preterm delivery
- Babies born so tend to have Respiratory issues, especially breathing difficulties.
- Stillbirth
- Obesity and development of Type 2 diabetes mellitus in later life (in child and mother)
Risk Factors of Diabetes
All types of diabetes have common risk factors. This doesn’t necessarily mean that an individual with any of the following factors can have diabetes, but the chances are invariably high. The common diabetes warning signs are:
- Obesity
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Family History: Parent with diabetes
- Prediabetic
- Pregnancy is one of the risk factors for Gestational diabetes.
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- Age of 45 or above
- Smoking
- Unhealthy diet
- Other chronic inflammatory conditions in the body
Tips to Manage Diabetes and Prevent Unnecessary Complications
Although diabetes is a chronic condition where complete reversal is questionable, the condition can be managed very well to keep life on a soundtrack. If you have diabetes, the following measures can help to manage diabetes and reduce unnecessary complications.
- Keep regular track of blood glucose levels.
- Take medications at the proper time.
- Don’t skip medications based on self-evaluations.
- Drink plenty of water and maintain a healthy and low-glucose diabetes diet.
- Stay active and work out at least 3-4 days a week.
- In case of getting wounded, treat properly and maintain a hygienic environment.
- Quit smoking and alcohol intake.
- If you are hypertensive or have high cholesterol levels, lowering these two is necessary for lowering blood glucose.
Conclusion
Diabetes is a chronic ailment that can necessarily cause an imbalance in everyday lifestyle. Having diabetic parents does not necessitate that you may have diabetes, but there is a slight chance of developing it if you have an unhealthy lifestyle. A sedentary lifestyle, unhealthy diet, and obesity pose a considerable risk for the occurrence of diabetes. Adopt an active and healthy lifestyle to reduce the chances of acquiring diabetes.