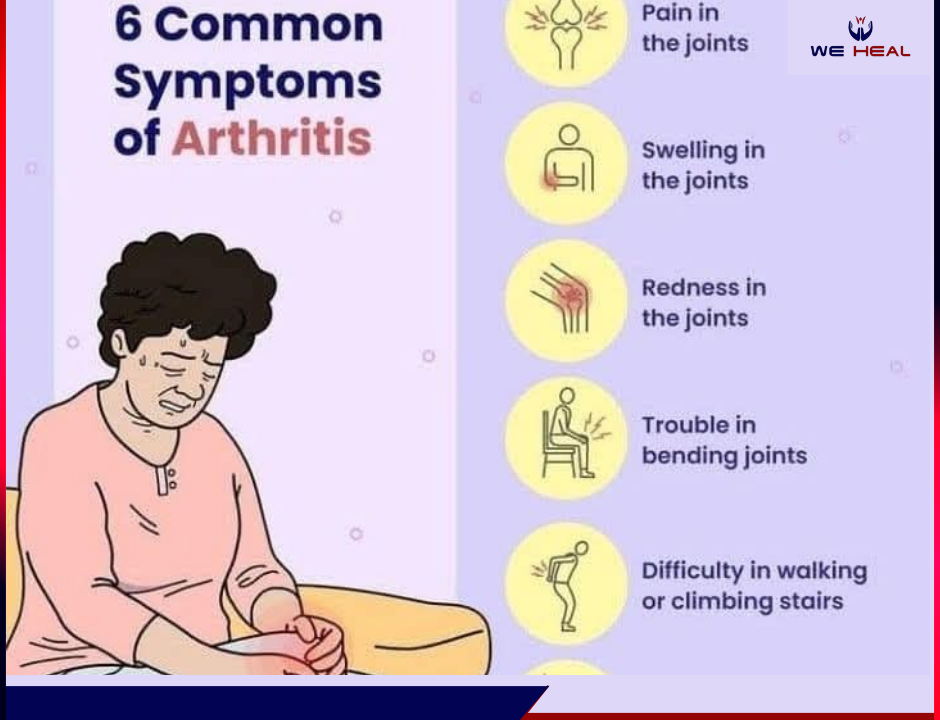
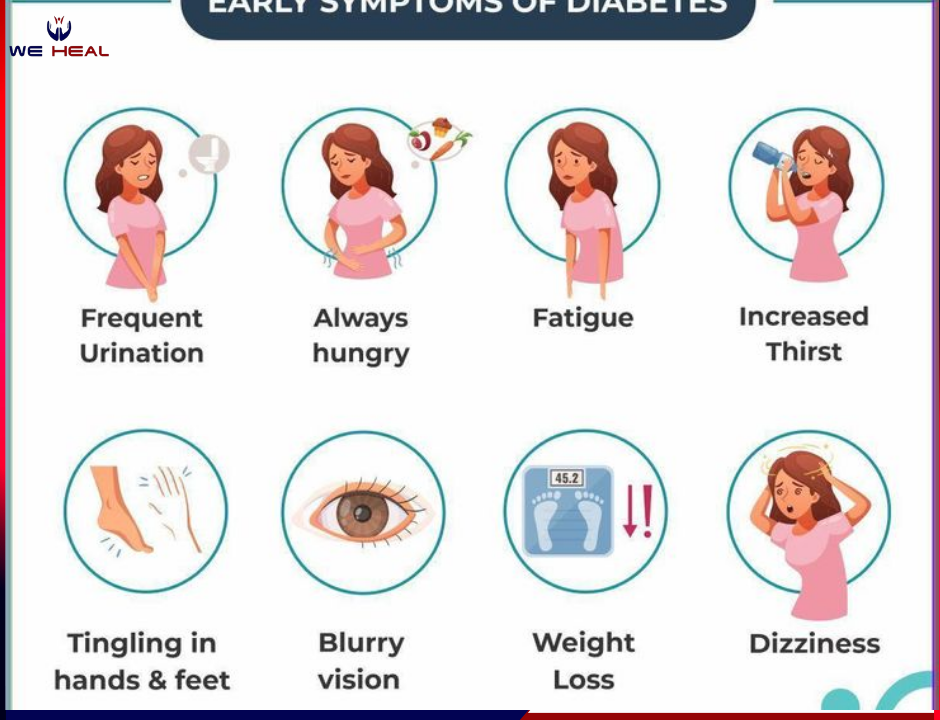
How to Drink Flavored Water Without Damaging Your Teeth
July 29, 2024
Can Dental Implants Cause Headaches?
August 19, 2024weight gain associated with thyroid disorders is uncertain. People who gain weight without evident cause, such as a swollen body or an uncomfortable amount of fat, may doubt if their issues are related to an obesity symptom or a thyroid issue. It is believed that weight gain can result from even minor modifications to thyroid function.
In reality, many women with thyroid test results reported as “normal” might still have subclinical hypothyroidism, which is sufficient to cause weight gain and other uncomfortable symptoms. Research has found that overweight or obesity was noticed in 76.5% of hypothyroid and 58.8% of hyperthyroid patients. Maintaining weight also frustrates many thyroid patients. This article explains why and how thyroid dysfunction impacts a person’s weight and what the relationship is between thyroid and weight management.
Role of Metabolism
Food is broken down by various types of processes in your metabolism and transformed into the energy your body needs to function. It also determines the rate at which your body burns calories. Genetics plays an important role in determining how efficiently your metabolism functions.
Engaging in physical activity and carrying out daily tasks burn calories. Even when you’re sleeping, your body continues to utilize energy. The efficiency with which it accomplishes this is referred to as basal metabolic rate (BMR). When you consume more food than your body can utilize, your body stores extra energy as fat, which causes you to gain weight.
Connection Between Thyroid and Weight Management
The thyroid is a small gland with a butterfly-like shape located in the front of the neck, beneath the Adam’s apple. This small organ is extremely significant because it produces hormones that help regulate the body’s growth, development, and metabolism.
Triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4), which both affect the body’s metabolism, are the primary hormones produced by this organ. These hormones have a significant impact on weight management because they regulate how the body uses energy and how quickly calories are burned. This significantly questions the thyroid and weight relationship.
How Does Hypothyroidism Affect Your Weight?
When the thyroid gland is underactive, it produces insufficient amounts of T3 and T4 hormones. This leads to the condition known as hypothyroidism, which affects approximately 100 individuals, the majority of whom are female. If left untreated, an underactive thyroid can raise the risk of female infertility. It ultimately leads to thyroid disease and obesity, along with depression-related disorders.
Signs and Symptoms of Hypothyroidism
The symptoms of hypothyroidism, or an underactive thyroid, can range widely and be mild to severe. Common symptoms include:
- Fatigue
- Weight gain
- Feeling cold
- Dry skin
- Hair changes
- Constipation
Thyroidism and obesity may also have an impact on the heart, leading to fatigue during exercise and a slower heart rate. Some women may have irregular menstruation and have trouble becoming pregnant.
How Does Hyperthyroidism Affect Your Weight?
Hyperthyroidism, or an overactive thyroid, causes an excessive amount of T3 and T4, which can speed up metabolism. Despite an increase in appetite, this higher metabolic rate can lead to thyroid and weight loss.
Given that patients with hyperthyroidism typically lose weight, 10% of them may gain weight instead. Although the impact of treatment on weight can vary, some research indicates that it may result in excessive weight gain.
Signs and Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism sometimes looks like other health problems. That may make diagnosis challenging. Among the numerous other symptoms are:
- Reducing weight naturally
- Tachycardia, or a rapid heartbeat
- An irregular heartbeat, also known as arrhythmia
- Heart pounding, also known as palpitations
- Increased appetite
- Anxiety, irritability, and nervousness
- Tremor, which is typically a slight shaking of the hands and fingers
- Sweating
- Changes in the menstrual cycle
- Increased heat sensitivity
- Changes in bowel habits, particularly increased frequency of bowel movements
- Thyroid gland enlargement, also known as a goiter, can cause swelling at the base of the neck.
- Fatigue
- Weakness of the muscles
Older adults are more likely to experience symptoms that are difficult to recognise.
When should See a Doctor?
Your primary care physician can diagnose and treat your thyroid and weight management, particularly if you have hypothyroidism. If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s a good idea to see a doctor for an evaluation.
- Unexplained Weight Changes: Significant weight gain or weight loss without any obvious reason.
- Fatigue and Lethargy: Feeling constantly tired or sluggish, even after rest.
- Sensitivity to Temperature: Being intolerant to cold or heat.
- Irregular Menstrual Cycles: For women, thyroid issues can disrupt menstrual cycles.
- Digestive Issues: Constipation or diarrhea can accompany thyroid disorders.
Final Words
Reaching and maintaining a healthy body weight depends on various interrelated factors, one of which is the thyroid gland’s general health. You must understand the connection between thyroid function and managing weight, irrespective of whether you have hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism. Optimizing the health of thyroid and weight management can be achieved by making thyroid-supportive behaviors a priority. These behaviors include eating a balanced diet, exercising frequently, and consulting a doctor for treatment of any underlying thyroid conditions.