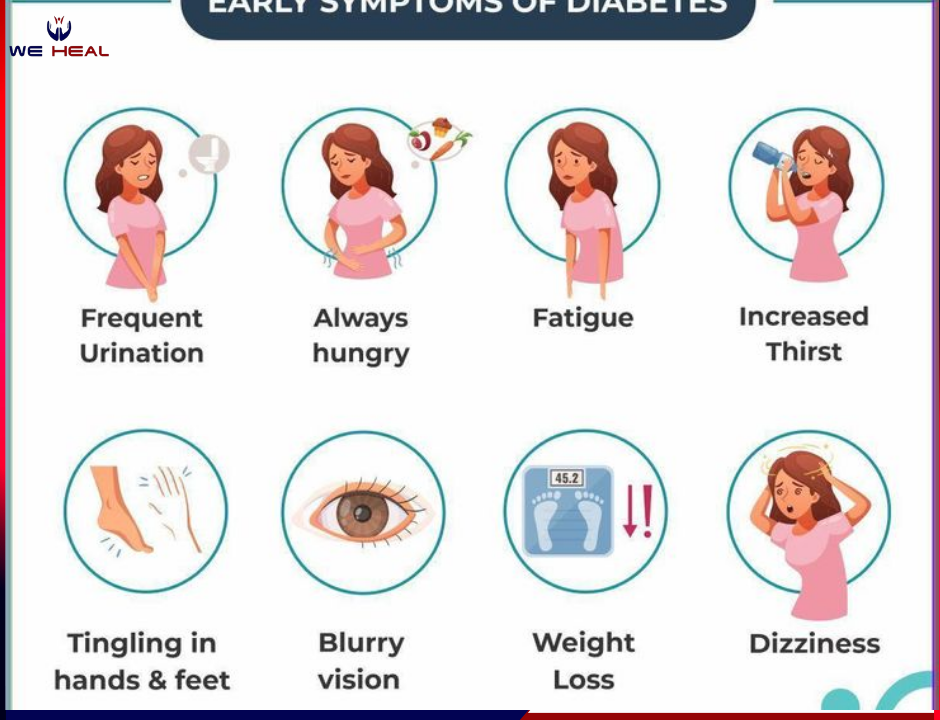
Dealing with Diabetes: Understanding, Controlling, and Preventing This Chronic Condition
March 11, 2024
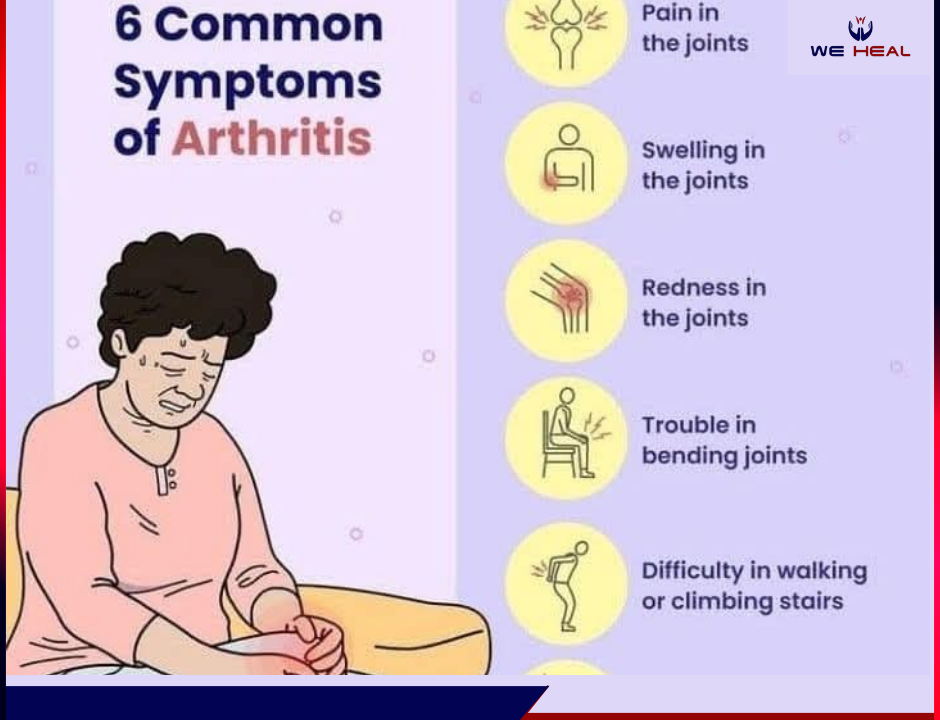
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Symptoms, Causes And Prevention-We Heal Clinic
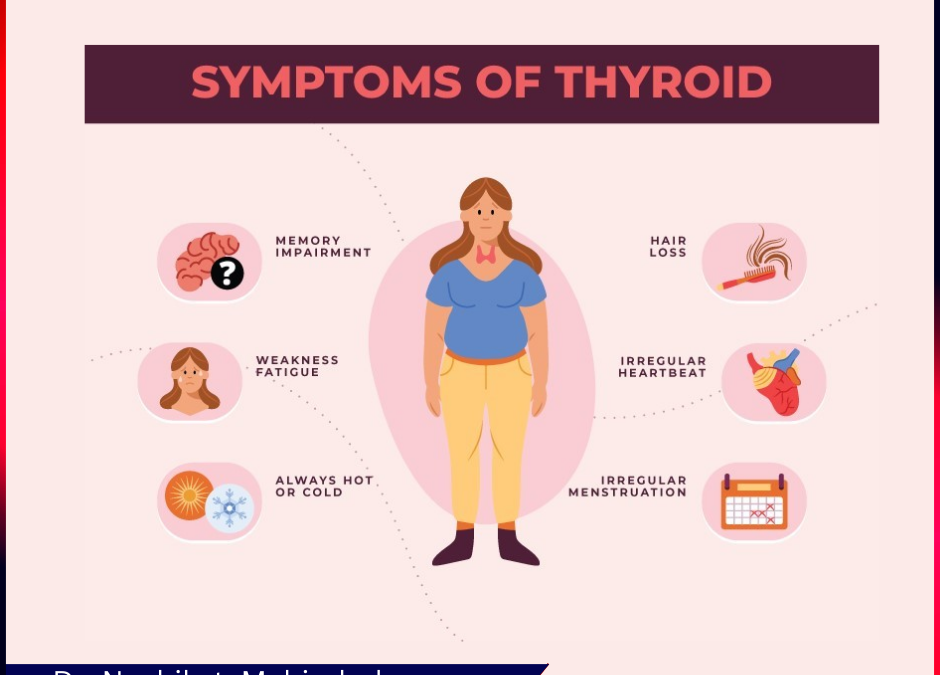
April 1, 2024The thyroid is a little gland in the neck that secretes hormones that control metabolism, growth, and development. There are millions of people suffering from thyroid dysfunction globally. We will talk about thyroid tests in this post, covering the many blood tests that measure thyroid levels, what they mean, and how they can be used to identify thyroid diseases.
What is the thyroid hormone?
The main hormone in charge of controlling how rapidly your metabolism functions is the thyroid hormone. The development of a baby’s brain depends on thyroid hormone. The two main hormones secreted by the thyroid gland, thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), are combined to form thyroid hormones.
Because T4 is generally inactive, meaning it has little effect on your cells, while T3 is active, they are frequently referred to as “thyroid hormone” together. Your body’s organs convert T4, which has been released by your thyroid, into T3, so that it can affect your cells and metabolism.
Types of Thyroid Blood Tests
Thyroid blood tests are the primary way to diagnose thyroid disorders. There are different types of thyroid blood tests, including:
- Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) test: The TSH test calculates the amount of TSH the pituitary gland produces. A high TSH level suggests an underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism), whereas a low TSH level indicates an overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism). TSH stimulates the thyroid gland to generate thyroid hormones.
- T4 (thyroxine) test: The T4 test measures the level of thyroxine hormone produced by the thyroid gland. A high T4 level indicates hyperthyroidism, while a low T4 level indicates hypothyroidism.
- T3 (triiodothyronine) test: The T3 test measures the level of triiodothyronine hormone produced by the thyroid gland. A high T3 level indicates hyperthyroidism, while a low T3 level indicates hypothyroidism.
- Thyroid antibody test: This examination examines the quantity of immune system-produced antibodies that target the thyroid gland. An autoimmune thyroid illness like Hashimoto’s thyroiditis or Graves’ disease may be indicated by high levels of thyroid antibodies.
Understanding Thyroid Test Results
Interpreting thyroid test results can be complex and requires the expertise of a healthcare provider. The common thyroid blood test (T3, T4, and TSH) measures the level of thyroid hormones in the blood. Normal reference ranges can vary between laboratories, but generally, a TSH level between 0.4 and 4.0 mIU/L is considered normal, while T4 levels should be between 4.5 and 11.2 mcg/dL and T3 levels between 80 and 200 ng/dL
Hypothyroidism test results indicate an underlying thyroid disorder. Further testing may be necessary to determine the cause. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider to interpret thyroid test results and recommend appropriate treatment based on individual needs.
Summary
Thyroid tests are essential for diagnosing and managing thyroid disorders. TSH, T4, and T3 tests can help identify the level of thyroid hormones in the blood, while thyroid antibody tests can identify autoimmune thyroid disorders.