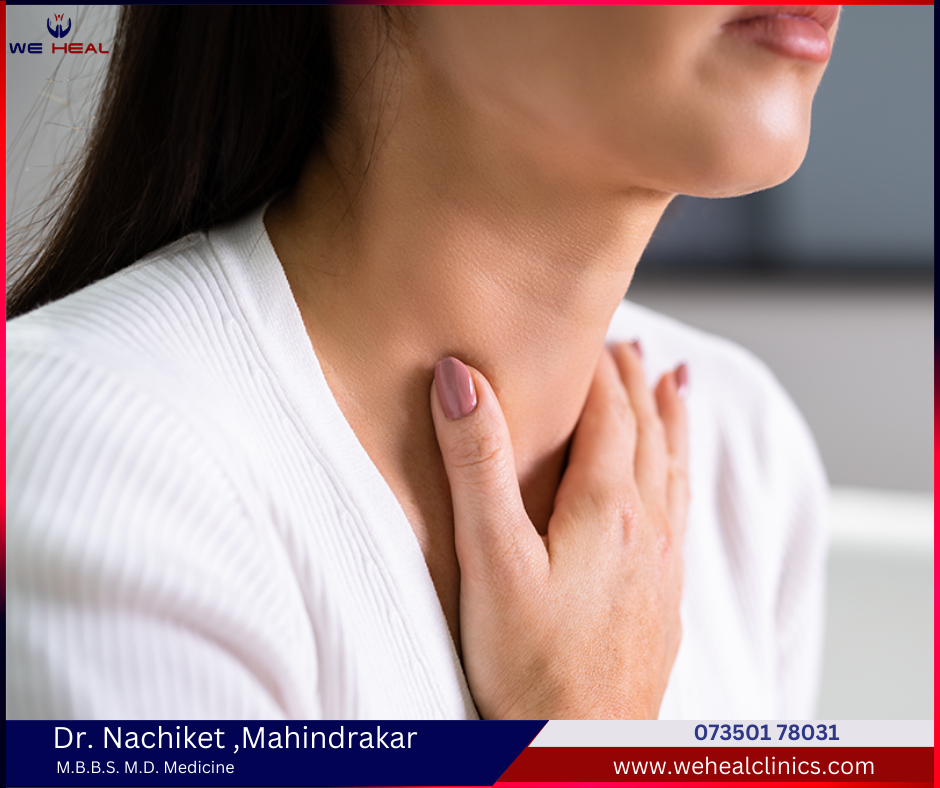
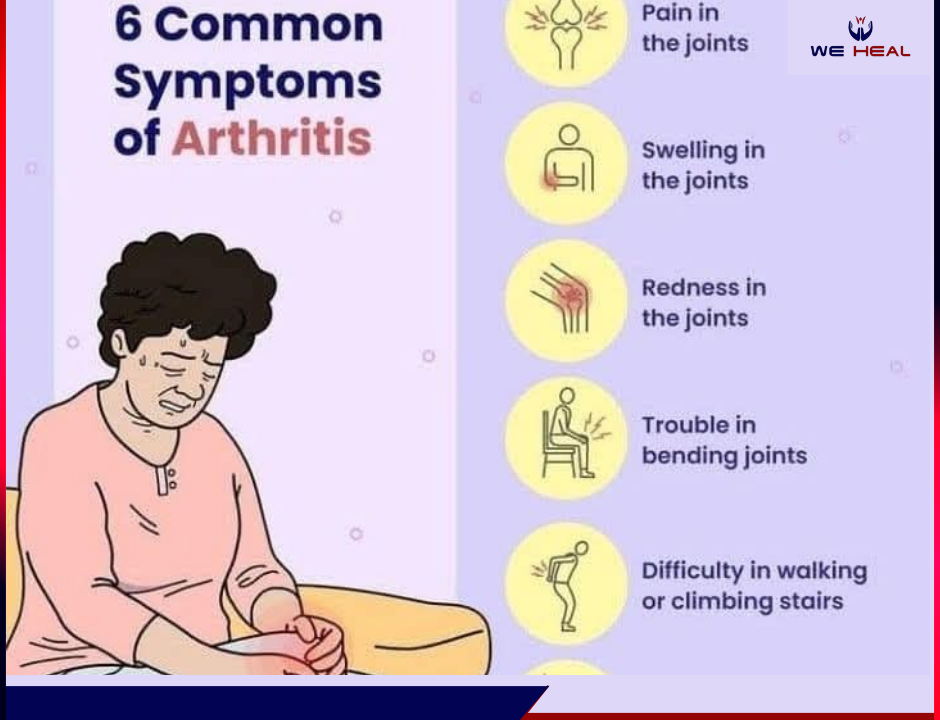
Goitre and Other Thyroid Swellings- We Heal Clinic
January 16, 2024
What Does Cosmetic Dental Treatment Mean?
February 5, 2024Type 2 diabetes and its causes
When you eat food, it is broken down and processed into glucose and other nutrients. Your pancreas makes a hormone called insulin that ensures this glucose reaches all the cells in the body for energy. However, when your cells do not respond normally to insulin, it results in insulin resistance.
To overcome this resistance, your pancreas produces more insulin to stimulate the cells to take up the glucose. Eventually, your pancreas gives up and stops producing adequate insulin. As a result, your blood sugar levels rise, resulting in type 2 diabetes.
High blood sugar levels are harmful to your body and a major risk factor for heart disease, vision loss and kidney problems.
Risk factors of type 2 diabetes
While you can develop type 2 diabetes at any age, it used to be more common among those over 45. However, in recent times, due to unhealthy dietary habits and sedentary lifestyles, this condition is increasingly becoming common in people under 35.
Besides age, a few factors that may increase your risk for type 2 diabetes include:
- Family history
- Being overweight or obese
- Lack of physical activity
- Gestational diabetes during pregnancy
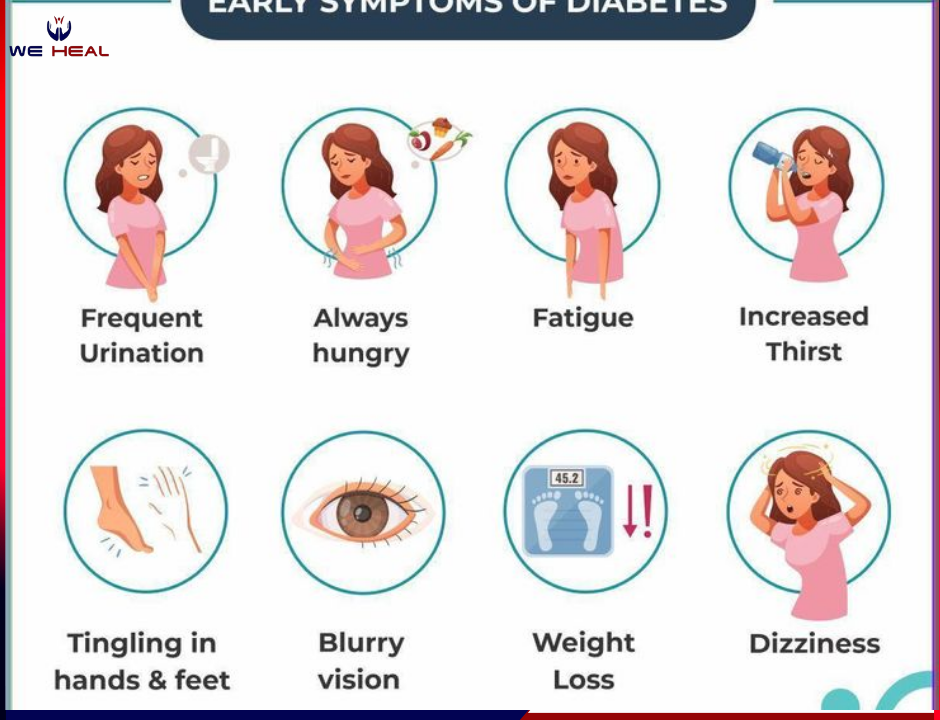
Symptoms of type 2 diabetes
In the early stages of type 2 diabetes (insulin resistance and prediabetes), you may not observe any signs or experience any symptoms. As the condition progresses, common type 2 diabetes symptoms appear and may include:
- Increased thirst and urination
- Increased hunger
- Fatigue
- Tingling sensation in hands and feet
- Blurring of vision
- Non-healing ulcers or wounds
- Unexplained weight loss
Since the symptoms of type 2 diabetes develop slowly, earlier symptoms are usually mild and difficult to identify. For this reason, doctors recommend getting your blood sugar levels checked at regular intervals during the year.
Early detection can help reverse prediabetes or send type 2 diabetes into remission, thereby preventing further health complications.
What are the complications of type 2 diabetes?
Untreated type 2 diabetes can result in a host of complications, such as:
- Digestive issues (like gastroparesis)
- Diabetic retinopathy
- Diabetic neuropathy
- Gum diseases
- Foot conditions like ulcers
- Heart disease
- Kidney and liver disease
- Liver conditions like non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- Urinary tract infections (UTI)
- Stroke
In severe cases of uncontrolled diabetes, it may result in a life-threatening condition called diabetic ketoacidosis.
Treatment and management of type 2 diabetes
Unfortunately, there is no cure for type 2 diabetes. However, with the right support from your doctor and healthcare team, you can maintain your blood sugar levels within the normal range. Management of type 2 diabetes typically involves:
- Medications to bring down your blood glucose levels
- Controlling blood pressure and cholesterol levels
- Eating a healthy diet rich in fibre, lean proteins and minimal carbohydrates and zero added sugar
- Regularly monitoring blood sugar levels
- Managing stress levels with deep breathing, meditation, yoga and mindfulness
- Exercising regularly
Can type 2 diabetes be prevented?
The good news is that type 2 diabetes can be prevented. Whether you have a high risk of developing the condition or have prediabetes, here are some ways to prevent type 2 diabetes:
- Eat a healthy, clean diet. You can seek help from a nutritionist who can guide you in choosing the right foods.
- Exercise regularly
- Lose weight and maintain it within the normal range